Abstract
Background: Follicular lymphoma (FL) is indolent and typically incurable, and patients (pts) often receive multiple lines of therapy (LOTs) throughout their lifetime (Batlevi et al. Blood Cancer J 2020). Options at relapse following first- or second-line anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (MoAb)-containing regimens remain limited, although approved third- and later-line therapies (3L+) have become available. Few studies have estimated the real-world economic burden of pts with relapsed/refractory (R/R) FL requiring 3L+ treatment. The aim of this study was to examine real-world healthcare resource utilization (HRU) and costs among pts receiving FL therapies in the 3L+ setting.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used administrative claims data from the IQVIA PharMetrics ® Plus, a US commercial claims database. Adult pts who had ≥1 inpatient claim or ≥2 outpatient claims with an FL diagnosis from January 1, 2011 to September 30, 2020 were included. The final 3L+ population was identified by combining two groups: (1) pts newly initiating FL treatment (defined as systemic anti-cancer therapies listed in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network [NCCN] guidelines) between January 1, 2012 and September 30, 2017 and receiving any subsequent 3L FL treatment during the study period; and (2) pts who received a NCCN-recommended 3L+ FL phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor (PI3Ki) between January 1, 2012 and March 30, 2020. Group 1 captured pts who received 3L FL therapies by a proxy algorithm for LOT (Optum 2018) based on NCCN guideline-listed therapies, and group 2 captured pts who received newer available PI3Kis, which are only approved in pts who have received ≥2 previous systemic FL therapies. The index date was the 3L treatment initiation date or the initial PI3Ki claim date. All pts had ≥12 months of pre- and ≥6 months of post-index continuous enrollment in medical and pharmacy benefits. Pts with other primary cancers or evidence of histological transformation during the pre-index period, or clinical trial participation during the study period were excluded. All-cause HRU and all-cause and FL-related (i.e. claim with a FL diagnosis in any position) costs (2020 USD) were annualized during the 3L+ treatment period (defined as the period from index 3L+ treatment until the end of the LOT) to mitigate the effects of different follow-up times.
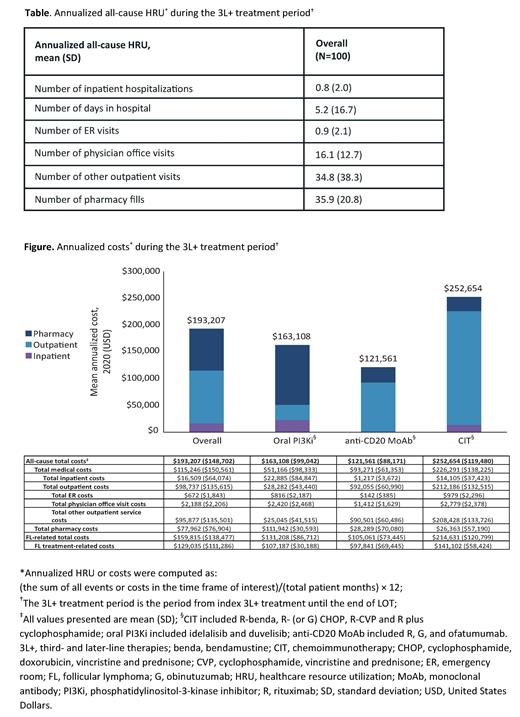
Results: Overall, 100 pts who initiated 3L+ FL treatment were included. Of these, 51% of pts were male, and the mean (standard deviation [SD]) age at index and Charlson Comorbidity Index (non-cancer) at baseline were 62 (10.1) years and 0.9 (1.5), respectively. Mean follow-up time was ~2.3 years, and the mean duration of index 3L+ FL treatment was 273 days. Overall, 44 pts (44%) received subsequent treatment. The most common therapy classes received for index 3L+ FL treatment were oral PI3Kis (n=45, 45%), anti-CD20 MoAb monotherapy (n=19, 19%), and chemoimmunotherapy (CIT; n=18, 18%). A summary of all-cause annualized HRU in pts receiving index 3L+ FL treatment is provided by visit type (Table). For all 3L+-treated pts, mean (SD) all-cause annualized total healthcare costs in the 3L+ treatment period were $193,207 ($148,702), and 83% of total healthcare costs were FL-related costs ($159,815 [$138,477]; Figure). Of the most common 3L+ FL therapy classes, CIT had the highest FL-related mean annualized costs ($214,631 [$120,799]), followed by oral PI3Kis ($131,208 [$86,712]), and anti-CD20 MoAb monotherapy ($105,061 [$73,445]).
Conclusions: The economic burden of pts with R/R FL requiring 3L+ FL treatment is substantial, with FL-related costs comprising the majority of total healthcare costs. More than 40% of the pts in this analysis needed subsequent treatment, further compounding the challenges faced by this high-risk population. This analysis provides an initial benchmark for ongoing and future evaluations of the economic value of currently available and emerging therapies for multiple relapsed FL, though future studies with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up are warranted.
Matasar: Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: Current Employment; Merck Sharp & Dohme: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company; Genentech, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Teva: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; IGM Biosciences: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Rocket Medical: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoVaccine Technologies: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria. Shapouri: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Genentech, Inc.: Current Employment. Ta: Genentech, Inc.: Current Employment. To: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months; Genentech, Inc.: Current Employment. Wu: Genentech, Inc.: Current Employment; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Wang: Genentech, Inc.: Current Employment; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Aurinia Pharmaceuticals Inc.: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Novavax, Inc.: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Oragenics, Inc.: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; The SPHERE Institute: Ended employment in the past 24 months; TG Therapeutics, Inc.: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal